In this article, you can find answers to frequently asked questions about the applications such as What is a Gastric Balloon, What is the Purpose of the Gastric Balloon Application, How Long after the Gastric Balloon is Removed, Does the Gastric Balloon Burst?
Gastric balloon is a non-surgical treatment method applied to the patients who have obesity problems but can be treated without surgery, except that they have a very high risk of life due to their excess weight and require surgery, but to lose some weight before the surgery and to enter the surgery in healthier conditions.
What are the Types of Gastric Balloons?
Gastric balloon is available in two types, endoscopic and swallowable.
The endoscopic gastric balloon changes every 6 months or 1 year. It is placed in the patient’s stomach after an average of 5-10 minutes of operation under sedation. It is filled with liquid and inflated, and it is aimed for the patient to eat less by taking up space in the stomach. When the time is up, the patient is put to sleep under sedation and removed endoscopically.
The swallowable gastric balloon is placed by allowing the patient to swallow without putting the patient to sleep. After the patient swallows the balloon, the balloon is inflated with liquid. It dissolves on its own in an average of 4-6 months and disappears in the body. Both methods need to be supported by diet.
What is the Purpose of Gastric Balloon Application?
Gastric balloon is performed endoscopically under light sedation.
The purpose of this application is to reduce the volume of the stomach relatively by placing a volume-filling, liquid-filled balloon inside the stomach, and accordingly, to reduce the daily food intake of the patient. With the application of the gastric balloon, the patient loses weight and a weight loss of 10-20 kg is expected.
Video Expression
How Long after the Gastric Balloon is Removed?
Generally, 6-month or 1-year balloons are applied. If this application is to lose some weight before the surgery or if the patient does not have too much weight, a 6-month balloon is preferred. With the effect of stomach acid, the balloon wall weakens by thinning and the risk of bursting increases, and the balloon should be removed after this period, preferably 6 months or 1 year, whichever type of balloon was used.
In summary, Gastric Balloon
- It is applied to overweight patients who do not need surgery to lose weight or who need surgery and need to lose some weight to reduce the risk before surgery.
- 10-20 kg weight loss is provided.
- It is done by endoscopy method, no surgical procedure is required
- Balloons with duration of 6 months or 1 year are used depending on the situation.
- At the end of the time, the balloons should be removed.
- The risk of bursting during the duration of the balloon is almost non-existent. Against the risk of explosion, some blue liquid is put into the balloon and in such a case, it is understood that the explosion has occurred by dyeing the urine blue.
- It is done by sleeping under sedation.
- The procedure is done in as little as 10 minutes.
- There is no need for hospitalization, you can return to daily life immediately.
- Nausea, vomiting and stomach cramps and severe pain can occur in the first week.
- In case of severe vomiting and pain despite the prescribed medications, the nearest health institution’s emergency service should be consulted without delay.

Does Gastric Balloon Burst?
During the period of 6-month or 1-year balloons, the risk of bursting is very, very low. However, the gastric balloon is filled with a blue liquid against the risk of the balloon bursting. The aim here is to understand that if the balloon bursts, a blue liquid comes out of the patient’s urine and the balloon bursts. In such a case, the patient should consult his/her doctor.
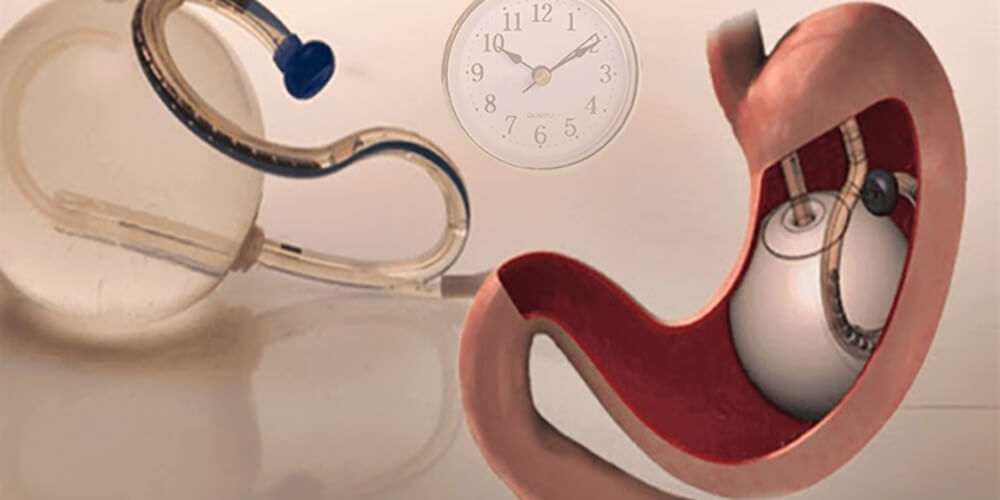

How Long Does Gastric Balloon Application Take?
This application is done under anesthesia. First, the patient is put to sleep with sedation, then the procedure is performed in 10 minutes. After the procedure, the patient comes to himself with rest for a while and can then return to his daily life.

The most important point in this application is that the possibility of nausea and vomiting that can occur in the first week should be explained to the patient before the procedure. Otherwise, the patient can perceive this normal situation as a serious health problem and panic.
When considering that the above-mentioned problems can arise, the necessary drugs are prescribed to the patient, but in some cases, these drugs cannot be sufficient in the first week. If very severe nausea, vomiting and pain are experienced during this procedure, the nearest health institution should be applied to the emergency. Here, the patient should be relieved and overcome this period by administering anti-nausea and pain relievers intravenously.

